What is an SSL certificate and what is it used for? What's the difference between SSL, TLS, and HTTPS?
What is an SSL certificate and what is it used for?
What's the difference between SSL, TLS, and HTTPS?
SSL Certificates are small data files that digitally bind a cryptographic key to an organization’s details. When installed on a web server, it activates the padlock and the https protocol and allows secure connections from a web server to a browser. Typically, SSL is used to secure credit card transactions, data transfer and logins, and more recently is becoming the norm when securing browsing of social media sites.
With an SSL certificate, data is encrypted prior to being transmitted via Internet. Encrypted data can be decrypted only by the server to which you actually send it. This ensures that the information you submit to websites will not be stolen.
Starting from 06/08/2014, Google announced that having an SSL certificate installed on your website will increase your ranking position, which is another great reason to use an SSL.
The certificate itself represents base64 encoded data that contains information about the entity the certificate was issued for, public key required for encryption and digital signature verification, and digital signature created with the private key of the certificate issuer.
certificate
An SSL certificate has to be installed on the server side. When you access a website secured by an SSL certificate issued by a trusted Certification Authority, you will see https:// at the beginning of its URL. Depending on the type of validation, a certificate applicant passed prior to the certificate issuance, a browser may also show the connection as secure by displaying a “lock” icon in the address bar:
or showing the name of your organization:
Types of SSL certificates
SSL certificates can be divided into 3 validation groups:
1.Domain Validation Certificates
Requires a certificate applicant to prove his/her control over the domain name only. The issued certificate contains a domain name that was supplied to the Certification Authority within the certificate request.
2.Organization Validation Certificates
Requires a certificate applicant to prove that his/her company is a registered and legally accountable business, and to pass domain validation. The issued certificate contains a domain and company name of the certificate applicant.
3.Extended Validation Certificates
Includes validation requirements of two validation types mentioned above and additional requirements. The issued certificate contains a domain and company name of the certificate applicant. It is worth mentioning that only Extended Validation certificates display a green bar with an owner’s company name in web browsers.
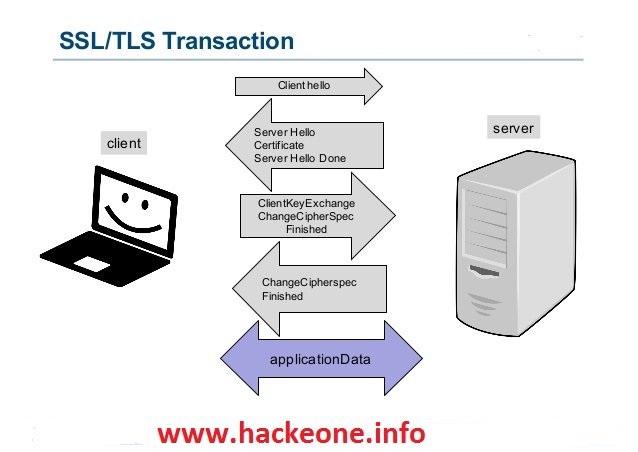
Whats the difference between SSL, TLS, and HTTPS?
Originally SSL was developed by Netscape Communications, for allowing secure connection of Web Browser & Web Server. The very first version of SSL has never been released due to some problems regarding the protection of credit card transactions over Internet. In 1994, again another version was created by Netscape named as SSLv2, which overcame the problem of first version and able to secure credit card number and other sensitive data and also offered the authentication of Web Server through the use of encryption and digital certificates. In 1995, Netscape furthered one more step and strengthened their cryptographic algorithms in order to resolve the problems related to SSLv2 and they released it under another version called SSLv3, which supports several other security algorithms which were not supported by SSLv2.
On the other hand, TLS (Transport Layer Security), is an updated and more secured version of SSL. In 1999, TLS 1.0 was released as a successor to SSL. TLS 1.0 was based on SSL 3.0 and is defined in RFC 2246 (Dierks & Allen, 1999).
TLS is very closely related to SSL 3.0, though it does not provide backward compatibility due to changes in some of the algorithms. Though one thing to note is that, in today's date also these security certificates are widely recognized as SSL, just because it's a more commonly used term, but in reality whenever someone buys an SSL certificate, they are actually buying the latest TLS certificates with the option of ECC, RSA or DSA encryption.
Later on TLS 1.0 was updated to v1.1 in RFC 4346 in 2006 (Dierks & Rescorla, 2006) and again to v1.2 in RFC 5246 in 2008 (Dierks & Rescorla, 2008). TLS is encryption for data in transit, not data at rest. That means that the end host or recipient in a TLS connection must be able to decrypt the encrypted traffic sent to it in order to be processed and/or displayed in the web browser.
HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer or HTTP over SSL. In this SSL acts as a sub layer under regular HTTP application layering. HTTPS encrypts an HTTP message prior to transmission and decrypts a message upon arrival.






No comments